Cervical Myelopathy Information
Cervical Spondolytic Myelopathy (CSM), or simply cervical myelopathy, is dysfunction of the spinal cord related to chronic abnormal pressure on the spinal cord. In simple terms there is chronic pressure on the spinal cord which causes it to not work properly. Unlike conditions that cause pressure on individual nerve roots, pressure on the spinal cord can result in loss of nerve function anywhere along the spinal cord below the compressed or damaged area. The effects of myelopathy can range from mild to severe, and can worsen over time. Any part of the spinal cord can be effected, however, it most commonly occurs in the cervical spine.
Cervical Spondolytic Myelopathy (CSM), or simply cervical myelopathy, is dysfunction of the spinal cord related to chronic abnormal pressure on the spinal cord. In simple terms there is chronic pressure on the spinal cord which causes it to not work properly. Unlike conditions that cause pressure on individual nerve roots, pressure on the spinal cord can result in loss of nerve function anywhere along the spinal cord below the compressed or damaged area. The effects of myelopathy can range from mild to severe, and can worsen over time. Any part of the spinal cord can be effected, however, it most commonly occurs in the cervical spine.
|
The most common cause of myelopathy is compression of the spinal cord by cervical stenosis (cervical spondylosis). This is narrowing of the spinal canal due to degeneration in the cervical spine. This is commonly due to disc degeneration and ligament thickening. Other causes of chronic spinal cord compression include:
Symptoms of cervical myelopathy range from very mild, with perhaps some tingling in the fingers, to extremely severe, with patients being wheelchair bound. Symptoms include:
|
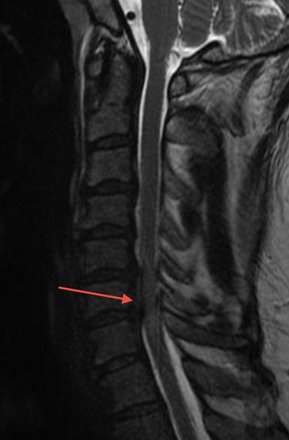
Image demonstrating a patient with pressure on the spinal cord at C5/6 and C6/7 due to disc prolapses (red arrow). The spinal cord at this level has white signal within it indicating severe compression and cord inflammation. This patient had weakness in the arms and legs with difficulty walking.
|
Cervical myelopathy is generally investigated with an MRI scan. Other investigations which may be helpful include:
- CT scan of spine
- X-rays - especially dynamic x-rays (flexion/extension x-rays) looking for spinal instability
- Nerve conduction studies and EMG
When the spinal cord is compressed and symptoms of cervical myelopathy have developed surgery is usually indicated. The exact type of surgery will depend on the cause of the myelopathy. Surgery generally involves a procedure such as a a cervical laminectomy or anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF). Both procedures aim to remove the pressure from the spinal cord. Dr Oehme will advise you which procedure is most appropriate for your condition.
|
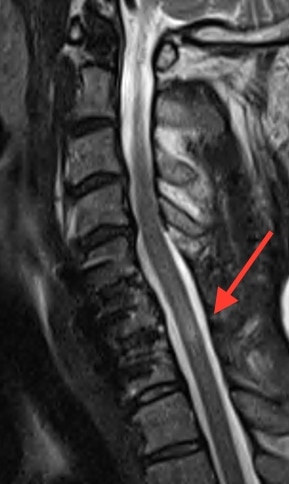
Image showing the same patient as above following successfull spine surgery. The spinal cord is now well decompressed with no pressure on it (red arrow). This patient underwent both an ACDF (C5/6 and C6/&) and a cervical laminectomy in order to adequately take the pressure of the spinal cord. Post operatively the patient recovered full movement and the ability to walk. |
For more information about cervical myelopathy and surgery to treat cervical myelopathy watch the videos below. See our spine surgery page for more information about cervical laminectomy or anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF).
Video about cervical myelopathy
Cervical myelopathy is a problem that affects your spinal cord. It happens when something presses harmfully against it. Your spinal cord is the main nerve pathway between your brain and your body. Pressure on it can cause problems throughout your body.
Video about cervical laminectomy
This procedure removes a section of bone from the rear of one or more vertebrae, called the lamina, to relieve the painful and disabling pressure of stenosis on the spinal cord. This procedure is performed from the back of the neck.
Video about anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF)
This surgery removes a herniated or diseased disc and relieves pressure on the spinal cord and nerve roots. This procedure is performed through a small procedure at the front of the neck.